Thinking of buying or leasing a vehicle for your business? How you use that vehicle—personally or for work—can significantly impact your tax deductions and benefits. Use it strictly for business? You may deduct 100% of the expenses. Mixing business and personal use? You’ll need to track carefully, and personal use could trigger taxable benefits. Let’s break it down.
How Vehicle Use Affects Tax Deductions and Benefits?
When it comes to vehicle financing, the way a vehicle is used—whether for business or personal purposes—greatly impacts the tax implications. Here’s an overview of how different financing options are affected:
1. Financing (Loan to Purchase the Vehicle)
- For Business-Only Use: If the vehicle is used exclusively for business, the full cost—including depreciation, fuel, maintenance, and insurance—can usually be deducted from the business’s taxable income. You can also claim full depreciation, either under the Capital Cost Allowance (CCA) in Canada, which reduces taxable income in the early years of ownership. Additionally, the interest on the loan is fully deductible as a business expense.
- For Mixed Business and Personal Use: The business can only deduct the portion of the vehicle’s costs related to its business use. For example, if 70% of the vehicle is used for business, 70% of expenses like depreciation and interest can be deducted. Personal use costs, such as fuel for personal trips, are not deductible, and taxable benefits may apply, such as in Canada, where personal use is considered a taxable benefit. Keeping accurate records of business vs. personal use is crucial.
2. Leasing
- For Business-Only Use: Lease payments are generally 100% deductible as an operating expense if the vehicle is used exclusively for business. This provides predictability in expenses, which can be beneficial if cash flow is a concern. However, no depreciation can be claimed since the vehicle is not owned.
- For Mixed Business and Personal Use: Similar to financing, only the business-use portion of lease payments is deductible. If the vehicle is 60% business and 40% personal, only 60% of the lease payments can be deducted. Additionally, personal use may result in taxable benefits, similar to financed vehicles.
3. Mileage Allowance (Per-Mile Reimbursement)
- For Business-Only Use: If an employee or owner uses their personal vehicle for business, they can be reimbursed for the business miles driven based on the standard mileage rate set by tax authorities. The business can deduct these reimbursements as a business expense.
- For Mixed Business and Personal Use: The business can only reimburse for mileage related to business travel. The employee or owner must maintain accurate records to distinguish between business and personal mileage.
4. Paying for Vehicle Expenses in the Corporation (Direct Payment for Vehicle Costs)
- For Business-Only Use: If the vehicle is used entirely for business, the business can pay for all vehicle-related expenses (fuel, insurance, repairs, etc.) and deduct them as business expenses. The business can also claim depreciation if it owns the vehicle.
- For Mixed Business and Personal Use: The business can only deduct the portion of expenses related to business use. For example, if 60% of the use is business-related, 60% of the vehicle’s expenses can be deducted. The personal use portion may be subject to taxable benefits, which need to be reported as income.
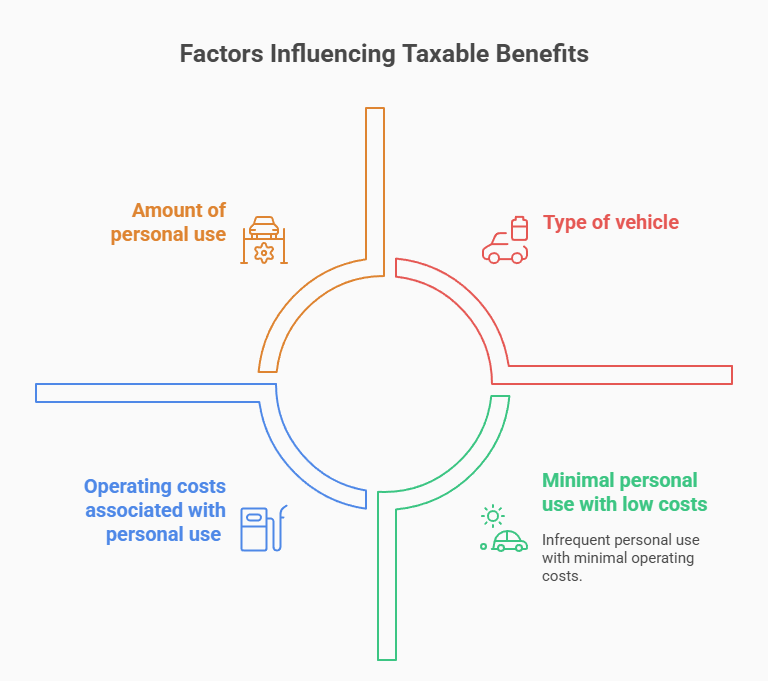
How Personal Use of a Company Vehicle Affects Your Taxes?
Regardless of how the vehicle is financed or leased, personal use of a company-owned vehicle often creates taxable benefits. These benefits are calculated based on several factors, such as the amount of personal use, the type of vehicle, and the operating costs associated with personal use. Some businesses may offer alternative allowances or reimbursements to reduce taxable benefits.
Key Takeaways
For Business-Only Use
- 100% of vehicle expenses can typically be deducted, including depreciation.
For Mixed Use
- Only the business portion of expenses is deductible, and personal use may result in taxable benefits.
Accurate record-keeping, such as a mileage log, is essential for proper tax deductions and reporting of taxable benefits.
Conclusion
The primary use of a vehicle impacts tax deductions and taxable benefits, with business-only use offering the most favorable tax treatment. However, when personal use is involved, proper tracking and reporting are essential to ensure compliance and minimize tax liabilities. Contact us today to optimize tax efficiency and ensure adherence to local laws.

